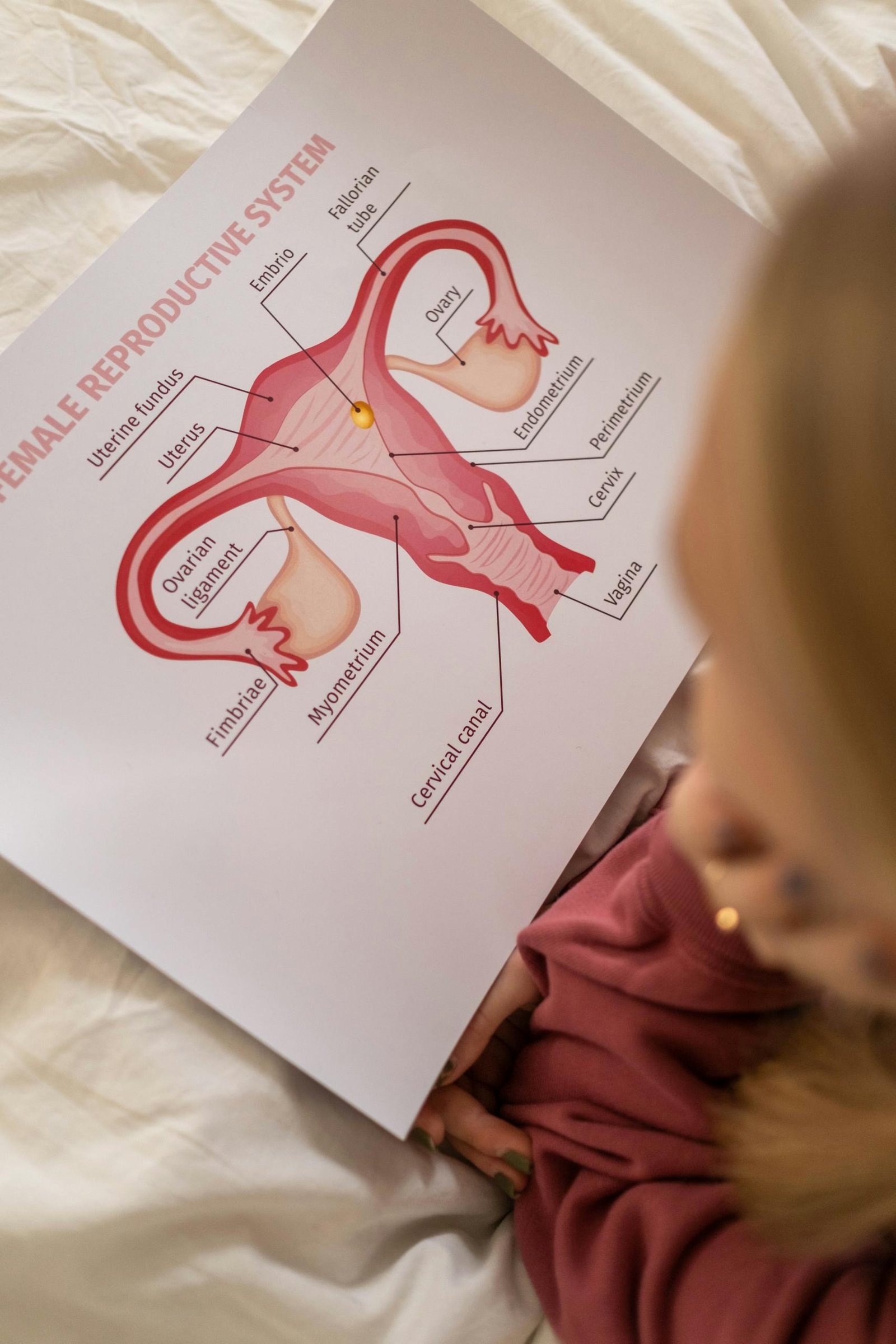
What is a fibroid?
A fibroid, also known as uterine fibroid, is a noncancerous growth of the uterus. Fibroids are made up of muscle and fibrous tissue and can vary in size. They can develop within the uterine wall, inside the uterine cavity, or on the outer surface of the uterus.
The exact cause of fibroids is unclear, but they are believed to be influenced by hormonal factors, particularly eostrogen and progesterone. Factors such as age, family history, ethnicity, and hormonal imbalances may contribute to their development.
While many women with fibroids may not experience any symptoms, others may have symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, and backache. The severity and type of symptoms can vary widely among individuals.
Treatment options for fibroids depend on the size, location, and symptoms. They can include medications to control symptoms, hormonal therapy, noninvasive procedures like uterine artery embolisation (UAE), and surgical options such as myomectomy (removal of the fibroids), hysterectomy (removal of the entire uterus) or a Laparotomy – A midline incision when the fibroid is too large to be removed the normal route. The choice of treatment is often based on the individual’s symptoms, age, desire for future fertility, and overall health.
Recovery is about 4 to 6 weeks depending on the individual with no driving and no lifting during that time.